Saturday, December 11, 2010
Link to Online Presentation
http://www.spicynodes.org/a/b4257df1293f85315c30e612757c6440
Thursday, December 9, 2010
Wednesday, December 8, 2010
HR (Staff)
· Annual HR (and Training) Budget: INR 60 Crores.
· Goal: Aims their technical skills and behavior to improve their efficiency and integration of individual and organization.
· Each employee has to undergo at least 1 week of training
· HRDI has specially trained some of its employees from the Institute of Human Behavior and Allied Sciences, Delhi à Aimed at future leaders at BHEL. The course covers the economic and industrial scenario, business policy, marketing strategies, finance, organization and individual and group development.
· Extension Programs for children and planning for retirement. The children workshops are nonresidential. This two-day workshop helps the children especially teenagers, understand themselves, identify their obstacles, teaches them how to resolve conflicts and develop trust. It even guides them in career opportunities.
· Training for those about to retire: This 3-day session helps the employees in looking after their finances, what kind of employment they would be able to find later, plus make them aware of how to look after their health through alternative therapies.
· BHEL has won the prestigious Golden Peacock award, given to corporate training houses by Institute of Directors.
· BHEL also contributes in the social development work such as adoption of backward villages, building and running of schools, medical centers, provides self-employment facilities for widows and challenged people.
Staff: Performance management

The key people involved in the process of mapping are:
Appraise: Identify appropriate KRAs, request for new KRAs (if required), Propose an action plan for achievement of each KRA and Assign a weightage for each KRA
Appraiser: Every executive who assesses the performance of one or more Appraises that report to him/her is an Appraiser.
Reviewer: Appraisers’ Appraiser, who is responsible for reviewing the entire performance process, is the Reviewer.
SOME KEY FACTS:
BHEL manufactures over 180 products under 30 major product groups and caters to core sectors of the Indian Economy viz., Power Generation & Transmission, Industry, Transportation, Telecommunication, Renewable Energy, etc. The wide network of BHEL's 14 manufacturing divisions, four Power Sector regional centres, over 100 project sites, eight service centers and 18 regional offices, enables the Company to promptly serve its customers and provide them with suitable products, systems and services -- efficiently and at competitive prices. The high level of quality & reliability of its products is due to the emphasis on design, engineering and manufacturing to international standards by acquiring and adapting some of the best technologies from leading companies in the world, together with technologies developed in its own R&D centres.
BHEL has acquired certifications to Quality Management Systems (ISO 9001), Environmental Management Systems (ISO 14001) and Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSAS 18001) and is also well on its journey towards Total Quality Management.
BHEL has:
Installed equipment for over 90,000 MW of power generation - for Utilities, Captive and Industrial users.
Supplied over 2,25,000 MVA transformer capacity and other equipment operating in Transmission & Distribution network up to 400 kV (AC & DC).
Supplied over 25,000 Motors with Drive Control System to Power projects, Petrochemicals, Refineries, Steel, Aluminum, Fertilizer, Cement plants, etc.
Supplied Traction electrics and AC/DC locos to power over 12,000 kms Railway network.
Supplied over one million Valves to Power Plants and other Industries.
BHEL's operations are organised around three business sectors, namely Power, Industry - including Transmission, Transportation, Telecommunication & Renewable Energy - and Overseas Business. This enables BHEL to have a strong customer orientation, to be sensitive to his needs and respond quickly to the changes in the market.
BHEL's vision is to become a world-class engineering enterprise, committed to enhancing stakeholder value. The company is striving to give shape to its aspirations and fulfill the expectations of the country to become a global player.
The greatest strength of BHEL is its highly skilled and committed 42,600 employees. Every employee is given an equal opportunity to develop himself and grow in his career. Continuous training and retraining, career planning, a positive work culture and participative style of management – all these have engendered development of a committed and motivated workforce setting new benchmarks in terms of productivity, quality and responsiveness.
BHEL manufactures over 180 products under 30 major product groups and caters to core sectors of the Indian Economy viz., Power Generation & Transmission, Industry, Transportation, Telecommunication, Renewable Energy, etc. The wide network of BHEL's 14 manufacturing divisions, four Power Sector regional centres, over 100 project sites, eight service centers and 18 regional offices, enables the Company to promptly serve its customers and provide them with suitable products, systems and services -- efficiently and at competitive prices. The high level of quality & reliability of its products is due to the emphasis on design, engineering and manufacturing to international standards by acquiring and adapting some of the best technologies from leading companies in the world, together with technologies developed in its own R&D centres.
BHEL has acquired certifications to Quality Management Systems (ISO 9001), Environmental Management Systems (ISO 14001) and Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSAS 18001) and is also well on its journey towards Total Quality Management.
BHEL has:
Installed equipment for over 90,000 MW of power generation - for Utilities, Captive and Industrial users.
Supplied over 2,25,000 MVA transformer capacity and other equipment operating in Transmission & Distribution network up to 400 kV (AC & DC).
Supplied over 25,000 Motors with Drive Control System to Power projects, Petrochemicals, Refineries, Steel, Aluminum, Fertilizer, Cement plants, etc.
Supplied Traction electrics and AC/DC locos to power over 12,000 kms Railway network.
Supplied over one million Valves to Power Plants and other Industries.
BHEL's operations are organised around three business sectors, namely Power, Industry - including Transmission, Transportation, Telecommunication & Renewable Energy - and Overseas Business. This enables BHEL to have a strong customer orientation, to be sensitive to his needs and respond quickly to the changes in the market.
BHEL's vision is to become a world-class engineering enterprise, committed to enhancing stakeholder value. The company is striving to give shape to its aspirations and fulfill the expectations of the country to become a global player.
The greatest strength of BHEL is its highly skilled and committed 42,600 employees. Every employee is given an equal opportunity to develop himself and grow in his career. Continuous training and retraining, career planning, a positive work culture and participative style of management – all these have engendered development of a committed and motivated workforce setting new benchmarks in terms of productivity, quality and responsiveness.
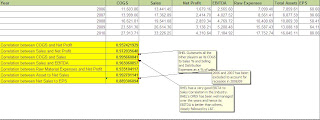
Financial Comparison Charts
EPS: Earnings per share serves as an indicator of a company's profitability. Earnings per share is generally considered to be the single most important variable in determining a share's price. It is also a major component used to calculate the price-to-earnings valuation ratio.
Profit Margins: A ratio of profitability calculated as net income divided by revenues, or net profits divided by sales. It measures how much out of every dollar of sales a company actually keeps in earnings. Profit margin is very useful when comparing companies in similar industries. A higher profit margin indicates a more profitable company that has better control over its costs compared to its competitors. Profit margin is displayed as a percentage; a 20% profit margin, for example, means the company has a net income of INR 0.20 for each Rupee of sales.
PBIT: Profit before interest and taxes ( PBIT ) or operating income is a investment formula to measure of a corporation's profitability by subtracting operating expenses from revenue excluding tax and interest.
DE Ratio: It is a measure of a company's financial leverage. A high debt/equity ratio generally means that a company has been aggressive in financing its growth with debt. This can result in volatile earnings as a result of the additional interest expense.
Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio: The fixed-asset turnover ratio measures a company's ability to generate net sales from fixed-asset investments - specifically property, plant and equipment (PP&E) - net of depreciation. A higher fixed-asset turnover ratio shows that the company has been more effective in using the investment in fixed assets to generate revenues.
Dividend Payout Ratio: The payout ratio provides an idea of how well earnings support the dividend payments. More mature companies tend to have a higher payout ratio.
ROCE: A ratio that indicates the efficiency and profitability of a company's capital investments. ROCE is used to prove the value the business gains from its assets and liabilities, a business which owns lots of land but has little profit will have a smaller ROCE to a business which owns little land but makes the same profit. It basically can be used to show how much a business is gaining for its assets, or how much it is losing for its liabilities.
Strategic Plans
Strategic Plan 2012
Objective: Become a US$10 Billion company by 2012
Action Areas:
• Identify potential future growth drivers in domestic and international market segments
• Have suitable product capabilities including manufacturing capacities and technologies
• Prepare the organization for competition through quality, low cost operations and efficiencies
• Assess and build enabling HRM & Financial Management
• Growth to be driven by capacity and capability enhancement
• Growth drivers are power, supported by its industry, transportation, transmission, exports and spares & services businesses
• Strategic initiatives to be undertaken like Design-to-cost, Purchase and Supply Management, Lean Manufacturing, etc.
Strategic Plan 2007
Objective: Achieve turnover of Rs. 125,000 million
Result: Achieved target turnover with a top line of Rs. 187,020 million
Action Areas:
• Positioning BHEL as an effective EPC contractor
• Attempting large projects through project partnerships
• Leveraging business through Govt. of India line of credit
• Product sales through distribution networks
Objective: Become a US$10 Billion company by 2012
Action Areas:
• Identify potential future growth drivers in domestic and international market segments
• Have suitable product capabilities including manufacturing capacities and technologies
• Prepare the organization for competition through quality, low cost operations and efficiencies
• Assess and build enabling HRM & Financial Management
• Growth to be driven by capacity and capability enhancement
• Growth drivers are power, supported by its industry, transportation, transmission, exports and spares & services businesses
• Strategic initiatives to be undertaken like Design-to-cost, Purchase and Supply Management, Lean Manufacturing, etc.
Strategic Plan 2007
Objective: Achieve turnover of Rs. 125,000 million
Result: Achieved target turnover with a top line of Rs. 187,020 million
Action Areas:
• Positioning BHEL as an effective EPC contractor
• Attempting large projects through project partnerships
• Leveraging business through Govt. of India line of credit
• Product sales through distribution networks
Tuesday, December 7, 2010
BHEL Strategic Initiative: Overseas Business
BHEL, ranking among the major power plant equipment suppliers in the world, is one of the largest exporters of engineering products & services from India. Over the years, BHEL has established its references in around 60 countries of the world, ranging from the United States in the West to New Zealand in the Far East. BHEL's export range covers individual products to complete Power Stations, Turnkey Contracts for Power Plants, EPC Contracts, HV/EHV Sub-stations, O&M Services for familiar technologies, Specialized after-market services like Residual Life Assessment (RLA) studies and Retrofitting, Refurbishing & Overhauling, and supplies to manufacturers & EPC contractors.
Critical Analysis of BHEL using McKinsey 7S
To critically analyze BHEL from the McKinsey 7S lenses, it is important to identify its vision. BHEL’s vision is “to become a world-class engineering enterprise, committed to enhancing stakeholder value”. Thus, from the vision we are clearly able to identify two distinct traits that BHEL wants to demonstrate during its lifetime (a) Become a world class engineering enterprise (b) Enhance stakeholder value.
A close look at each of these traits identifies the fact that, while becoming a world class engineering enterprise is an outside-in focus where BHEL would require to benchmark its internal processes, production systems, design principles, quality systems etc. with the other leaders in its industry and hence keep improving on it continuously. The fact that BHEL wants to enhance its stakeholder’s value involves an inside-out focus, where BHEL needs to determine how it will be able to generate enough value for its investors such that BHEL remains the destination of choice for investment. To e able to do this, BHEL would have to continuously set benchmarks and out-perform itself to be able to keeps investors interested.
Now to look at how BHEL has been able to achieve/work towards its dual element vision, we will utilize McKinsey’s 7S framework and try to identify which of the ‘S’s have been worked upon by BHEL and in what ways:
Skills
• BHEL has historically invested in its talent pool and have been able to attract the brightest and best. With a base of 42000+ skilled and committed employees, BHEL has went on to become the largest engineering and manufacturing enterprise in India operating from over 40 yrs and manufacturing over 180 products across 30 major product groups.
A close look at each of these traits identifies the fact that, while becoming a world class engineering enterprise is an outside-in focus where BHEL would require to benchmark its internal processes, production systems, design principles, quality systems etc. with the other leaders in its industry and hence keep improving on it continuously. The fact that BHEL wants to enhance its stakeholder’s value involves an inside-out focus, where BHEL needs to determine how it will be able to generate enough value for its investors such that BHEL remains the destination of choice for investment. To e able to do this, BHEL would have to continuously set benchmarks and out-perform itself to be able to keeps investors interested.
Now to look at how BHEL has been able to achieve/work towards its dual element vision, we will utilize McKinsey’s 7S framework and try to identify which of the ‘S’s have been worked upon by BHEL and in what ways:
Skills
• BHEL has historically invested in its talent pool and have been able to attract the brightest and best. With a base of 42000+ skilled and committed employees, BHEL has went on to become the largest engineering and manufacturing enterprise in India operating from over 40 yrs and manufacturing over 180 products across 30 major product groups.
• Following are the major areas of skill focus by BHEL: Thermal Power, Gas based Power, Hydro Power, DG Power, Industrial turbo sets, Boilers & Boiler Auxiliaries, Heat exchangers & Pressure vessels, Pumps, Power station control equipments, Oil field equipments, Transformers & Switch gears, Wind mills, Industrial electrical machines, Non-conventional energy systems, Casting & Forgings, Transportation equipment and Power devices.
• BHEL is a market leader in Power generation and Industrial electrical machines internationally.
Staff
• BHEL believes in investing in its employees and thus have created a culture of continuous learning which enables them to be at the cutting edge of technology changes. BHEL is able to pursue this by:
o Continuous training and retraining
o Career planning for its employees
o Positive work culture and participative style of management
All these have engendered development of a committed and motivated workforce setting new benchmarks in terms of productivity, quality and responsiveness.
• BHEL has joined the Global Compact of United Nations which includes the following principles
o Human Rights
Business should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights
Make sure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses
o Labour Standards
Business should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining
The elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labour
The effective abolition of child labour
The elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation
Shared Values
• As stated in its vision, BHEL has a strong focus on generating value for its stakeholders. This can be adjudged by the fact that the company has been earning profits continuously since 1971-72 and paying dividends since 1976-77.
• BHEL has a strong commitment towards environment and pollution control. Hence it has set up PCRI which is the in-house R&D unit of BHEL. The institute has undertaken a number of R&D projects to develop industrial pollution control technologies, such as:
o Development of prediction modes for forecasting air pollution
o Development of Acoustic barriers to control noise pollution in Fabrication shops
o Development of technology for disinfection of treated sewage using ultra violet radiation techniques
• BHEL supports anti-corruption practices and demonstrates it by participating in Global Compact of United Nations which includes Anti-corruption principles.
Systems
• Quality Management:
o BHEL uses Quality Management Systems, which are certified to ISO 9001:2000 series of Standards by Internationally acclaimed certifying agency, BVQI to meets its Quality policy.
o Corporate Quality and Unit level Quality structure enables requisite planning, control and implementation of Company-wide Quality Policy and Objectives which are linked to the Company's Vision statement
o Corporate Quality derives strength from direct reporting to Chairman and Managing Director of the Company.
o BHEL utilizes and propagates Quality Management Systems and Total Quality Management
o As part of its quality initiative BHEL formulates, implements and monitors improvements plans with focus on internal and external Customer Satisfaction. It performs investigations and preventive actions on Critical Quality Issues.
o Calibration and testing laboratories of BHEL are accredited under the National Accreditation Board for Calibration and Testing Laboratories (NABL) scheme of Laboratory Accreditation, which has got mutual recognition with Asia Pacific Laboratory Accreditation Conference and International Laboratory Accreditation Conference.
o BHEL has achieved product certification from international bodies like ASME, API etc. and Plant Approvals by agencies like Lloyds Register of Shipping, U.K., Chief Controller of Explosives India, TUV Germany etc.
o BHEL has adopted European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) model for Business Excellence. Through this model and annual self-assessment exercise, BHEL is institutionalising continuous improvement in all its operations.
• Vendor Management
o Vendor awareness is driven through online systems which makes the vendor bill payment processes transparent.
o Vendor on-boarding is being made easy by making vendor registration & information systems available online.
Strategy
o BHEL has participated in strategic alliances and JVs which has allowed them to expand their product offerings and improve technology capability by undertaking joint R&D projects with its partners. Some of the key alliances/JVs are as follows:
o BHEL and GE India Industrial Private Limited (GEIIPL), a 100% owned subsidiary of GE, USA, have joined hands for cooperation on Water Treatment Equipment. As per the agreement, BHEL and GEIIPL will jointly engineer and supply water treatment solutions for the Indian market. Over the term of the agreement, through joint working, BHEL will acquire the capability to address large water treatment systems based on GE Products, on its own.
o BHEL and Govt. of Kerala form JV for manufacture of products for Railways and Industries. Strategic move to enhance BHELs presence in the Transportation, Industrial and Renewable Energy Sectors.
o BHEL and Toshiba Corporation sign MoU to form JV Company for Transmission and Distribution business in India and other mutually agreed countries.
o BHEL and MPPGCL float JV Company for setting up Supercritical Thermal Power Project in Madhya Pradesh.
o BHEL and KEL to form JV for manufacture of products for Railways and Industries; Strategic move to enhance BHEL's presence in the Transportation, Industrial and Renewable Energy Sectors
o BHEL and TNEB float JV Company for setting up the first 2x800 MW Supercritical Power Project in Tamil Nadu.
o BHEL, NTPC JV Company Incorporated, To jointly execute EPC Contracts and Manufacture and Supply Equipment in India and Abroad
o BHEL makes its foray in execution of Supercritical Thermal Power Projects; Signs MoU with TNEB to float JV Company for setting up the first 2x800 MW Supercritical Power Project in Tamil Nadu.
o R&D and technology development are of strategic importance to the company as it operates in a competitive environment where technology is a key driver. Technology development efforts undertaken by BHEL have led to the filing of patents and copyrights at the rate of nearly one a day, significantly enhancing the company’s intellectual capital to almost 1,300 patents and copyrights filed, which are in productive use in the company’s business.
With an R&D spend at nearly 2.5% of its sales turnover; BHEL is the highest spender on R&D in India for its kind of industry. Significantly, BHEL is one of the only four Indian companies and the only Indian Public Sector Enterprise figuring in ‘The Global Innovation 1000’ of Booz & Co., a list of 1000 publicly-traded companies which are the biggest spenders on R&D in the world.
o BHEL plans to invest and build competency in emerging markets which includes Alternative energy, transformer manufacturing (increased to 45,000 MVA), investment of Rs. 250 crores in CE (areas identified are Photovoltaic, Sub-assembly, Defense products & Semiconductors. New product investments in PADO hydro & gas, 800mw sets, railway signaling, space grade solar cells, ships control system and integrated platform management system
Become Innovation leader through Talent enhancement
BHEL has envisioned to becoming " A world – class innovative , competitive and profitable engineering enterprise , providing total business solutions ". For realizing this vision , continuous development and growth of the 47000 strong highly skilled and motivated people making the organization , is the only 'mantra'.
Human Resource Development Institute ( HRDI ) , the corporate training institute of the company , in association with the advanced technical education center ( ATEC ) in Hyderabad and Human Resource Development Center at the units , is responsible for the total human resource development of the company. Further , competency development / assessment center for senior executive is taken up by HRDI.
Human Resource Development Institute ( HRDI ) , the corporate training institute of the company , in association with the advanced technical education center ( ATEC ) in Hyderabad and Human Resource Development Center at the units , is responsible for the total human resource development of the company. Further , competency development / assessment center for senior executive is taken up by HRDI.
Steps on Recruitment Process by BHEL
The recruitment process consist of the following steps:
• Generally begins when the personnel department receives requisitions for recruitment from any department of the company the personnel requisitions contains detail about the positions to be filled. number of persons to be recruited, required from the candidate, terms and conditions of employment and at the time by which the persons should be available appointment etc.
• Locating and developing the sources of required number and type of employees.
• Identifying the prospective employees with required characteristics.
• Communicating the information about the organization, the job and the terms and conditions of service.
• Encouraging the identified candidates to apply for jobs in the organization.
• Evaluating the effectiveness of recruitment process.
• Generally begins when the personnel department receives requisitions for recruitment from any department of the company the personnel requisitions contains detail about the positions to be filled. number of persons to be recruited, required from the candidate, terms and conditions of employment and at the time by which the persons should be available appointment etc.
• Locating and developing the sources of required number and type of employees.
• Identifying the prospective employees with required characteristics.
• Communicating the information about the organization, the job and the terms and conditions of service.
• Encouraging the identified candidates to apply for jobs in the organization.
• Evaluating the effectiveness of recruitment process.
R&D and Innovation are strategic initiatives from BHEL
To remain competitive and to meet customer's expectations , BHEL lays great emphasis on the continuous up gradation of the products and related technologies , and development of new products. The company has upgraded its products to contemporary levels through continuous in – house efforts as well as through acquisition of new technologies from leading engineering organization of the world.
BHEL'S investment in R & D is amongst the largest in the corporate sector in India. Products developed in - house during the last five years contributed over 7% to the revenues in 2004 - 05.
BHEL has introduced , in the recent past , several state - of – the – art products ; low - NOx oil / gas burners , large capacity atmospheric fluidized bed combustion boilers , high - efficiency pelton hydro turbines , petroleum deport automation systems , 36 KV gas - insulated sub – station , controlled shunt reactors ( CSR ) and performance analysis , diagnostics and optimization ( PADO ) package for power plants , etc. The company has also transferred a few technologies developed in - house to other Indian companies for commercialization.
The company is also engaged in research in futuristic areas , such as applications of super conducting materials in power generation and industry , and fuel cells distributed , environment – friendly power generation.
BHEL'S investment in R & D is amongst the largest in the corporate sector in India. Products developed in - house during the last five years contributed over 7% to the revenues in 2004 - 05.
BHEL has introduced , in the recent past , several state - of – the – art products ; low - NOx oil / gas burners , large capacity atmospheric fluidized bed combustion boilers , high - efficiency pelton hydro turbines , petroleum deport automation systems , 36 KV gas - insulated sub – station , controlled shunt reactors ( CSR ) and performance analysis , diagnostics and optimization ( PADO ) package for power plants , etc. The company has also transferred a few technologies developed in - house to other Indian companies for commercialization.
The company is also engaged in research in futuristic areas , such as applications of super conducting materials in power generation and industry , and fuel cells distributed , environment – friendly power generation.
Team Meeting
Hi Team,
As discussed, the team meeting has been planned for today 7th Dec, 20010 at 11:30 PM. Please comment to let us know your presence.
As discussed, the team meeting has been planned for today 7th Dec, 20010 at 11:30 PM. Please comment to let us know your presence.
SWOT Analysis BHEL
SWOT (Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis of BHEL:
Strengths:
• Sound engineering base and ability to assimilate
• Relatively stable industrial relationship
• Access to contemporary technologies with the support from renowned collaborators.
Ability to set up power plants on turnkey basis, complete know- how for manufacture of entire equipment is available with the company.
• Ability to manufacture or procure to supply spares.
• Fully equipped to take capital maintenance and servicing of the power plants.
• Largest source of domestic business leading to major presence and influence in the
market.
• Ability to successfully overhaul and renovate power stations equipment of different
international companies.
• Low labour cost.
• For non- BHEL products, services and spares are not easily available and if they are,price charged are very high.
• Sound financial position in terms of profitability and solvency.
• Low debt equity ratio (even lower than 0.5:1) for all the years under study, enabling company to raise capital.
Weaknesses:
• Difficulty in keeping up the commitments on the product delivery and desired sequence
of supplies.
• Larger delivery cycles in comparison with international suppliers of similar equipment.
• Inability to provide supplier’s credit, soft loans and financing of power projects.
• Lack of effective marketing infrastructure.
• Due to poor financial position of state electricity boards, which are the major customers of BHEL in India, liquidity position of BHEL is not satisfactory.
• Being a public sector company BHEL is suffering from sub optimality of control due to:
1. Displacement of social objectives by political objectives, which may lead to
redundant costs and also rising costs.
2. Direct political intervention in managerial decision over an arm length relationship
that would restrict government’s task of setting appropriate managerial incentive
structure.
3. Private goals that lead to budget growth and employment growth.
4. Internal inefficiencies in bureaucratic activity.
Opportunities:
• Demand for power and hence plant equipment is expected to grow.
• Private sector power plants to offer expanded market as utilities suffers resource crunch.
• Ageing power plants would give rise to more spares and services business.
• Life expansion program for old power stations.
• Export opportunities.
• Easy processing of joint ventures/ collaboration/import/ acquisition of new technology.
• Financial and operational autonomy for profit making public sector enterprises. To make the public sector more efficient government has decided to grant enhanced autonomy and delegation of powers to the profit making public sector enterprises.
Threats:
• Increased competition both national and international.
• Multilateral agencies reluctant to lend to power sector because of poor financial
management of S.E.Bs
• More concessions to private sector and not to government owned utilities like NTPC or S.E.Bs, so future power projects would be opened up in private sector.
• Level playing ground not available, foreign companies spending much more on business promotion tactics.
Strengths:
• Sound engineering base and ability to assimilate
• Relatively stable industrial relationship
• Access to contemporary technologies with the support from renowned collaborators.
Ability to set up power plants on turnkey basis, complete know- how for manufacture of entire equipment is available with the company.
• Ability to manufacture or procure to supply spares.
• Fully equipped to take capital maintenance and servicing of the power plants.
• Largest source of domestic business leading to major presence and influence in the
market.
• Ability to successfully overhaul and renovate power stations equipment of different
international companies.
• Low labour cost.
• For non- BHEL products, services and spares are not easily available and if they are,price charged are very high.
• Sound financial position in terms of profitability and solvency.
• Low debt equity ratio (even lower than 0.5:1) for all the years under study, enabling company to raise capital.
Weaknesses:
• Difficulty in keeping up the commitments on the product delivery and desired sequence
of supplies.
• Larger delivery cycles in comparison with international suppliers of similar equipment.
• Inability to provide supplier’s credit, soft loans and financing of power projects.
• Lack of effective marketing infrastructure.
• Due to poor financial position of state electricity boards, which are the major customers of BHEL in India, liquidity position of BHEL is not satisfactory.
• Being a public sector company BHEL is suffering from sub optimality of control due to:
1. Displacement of social objectives by political objectives, which may lead to
redundant costs and also rising costs.
2. Direct political intervention in managerial decision over an arm length relationship
that would restrict government’s task of setting appropriate managerial incentive
structure.
3. Private goals that lead to budget growth and employment growth.
4. Internal inefficiencies in bureaucratic activity.
Opportunities:
• Demand for power and hence plant equipment is expected to grow.
• Private sector power plants to offer expanded market as utilities suffers resource crunch.
• Ageing power plants would give rise to more spares and services business.
• Life expansion program for old power stations.
• Export opportunities.
• Easy processing of joint ventures/ collaboration/import/ acquisition of new technology.
• Financial and operational autonomy for profit making public sector enterprises. To make the public sector more efficient government has decided to grant enhanced autonomy and delegation of powers to the profit making public sector enterprises.
Threats:
• Increased competition both national and international.
• Multilateral agencies reluctant to lend to power sector because of poor financial
management of S.E.Bs
• More concessions to private sector and not to government owned utilities like NTPC or S.E.Bs, so future power projects would be opened up in private sector.
• Level playing ground not available, foreign companies spending much more on business promotion tactics.
Friday, November 26, 2010
Artifacts Addition
Please take a look at the new artifacts that I have posted
7s Questions
7s Checklist Questions : Here are some of the questions that we need to explore to 7S framework and apply to BHEL. Using the information we can probably examine where there are gaps and inconsistencies between elements.
Strategy
What is BHEL strategy?
How do they intend to achieve their objectives?
How do they deal with competitive pressure?
How are changes in customer demands dealt with?
How is strategy adjusted for environmental issues?
How do they intend to achieve their objectives?
How do they deal with competitive pressure?
How are changes in customer demands dealt with?
How is strategy adjusted for environmental issues?
Structure
How is the company/team divided?
What is the hierarchy?
How do the various departments coordinate activities?
How do the team members organize and align themselves?
Is decision making and controlling centralized or decentralized? Is this as it should be, given what they're doing?
Where are the lines of communication? Explicit and implicit?
What is the hierarchy?
How do the various departments coordinate activities?
How do the team members organize and align themselves?
Is decision making and controlling centralized or decentralized? Is this as it should be, given what they're doing?
Where are the lines of communication? Explicit and implicit?
Systems
What are the main systems that run the organization? (We need to consider financial and HR systems as well as communications and document storage).
Where are the controls and how are they monitored and evaluated?
What internal rules and processes does the team use to keep on track?
Where are the controls and how are they monitored and evaluated?
What internal rules and processes does the team use to keep on track?
Shared Values
What are the core values?
What is the corporate/team culture?
How strong are the values?
What are the fundamental values that the company/team was built on?
What is the corporate/team culture?
How strong are the values?
What are the fundamental values that the company/team was built on?
Style
How participative is the management/leadership style?
How effective is that leadership?
Do employees/team members tend to be competitive or cooperative?
Are there real teams functioning within the organization or are they just nominal groups?
How effective is that leadership?
Do employees/team members tend to be competitive or cooperative?
Are there real teams functioning within the organization or are they just nominal groups?
Staff
What positions or specializations are represented within the team?
What positions need to be filled?
Are there gaps in required competencies?
What positions need to be filled?
Are there gaps in required competencies?
Skills
What are the strongest skills represented within the company/team?
Are there any skills gaps?
What is the company/team known for doing well?
Do the current employees/team members have the ability to do the job?
How are skills monitored and assessed?
Are there any skills gaps?
What is the company/team known for doing well?
Do the current employees/team members have the ability to do the job?
How are skills monitored and assessed?
Monday, November 22, 2010
Disclaimer
This is an experimental / educational blog created by MPE (Batch 4) students of NMIMS, Bangalore to map BHEL's story using Mckinsey 7s.
This blog DOES NOT in any way, shape or form have an endorsement from BHEL and is purely based on facts available in the public domain.
This blog DOES NOT in any way, shape or form have an endorsement from BHEL and is purely based on facts available in the public domain.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)